More transparency, greater accountability and use of enforcement authority could help prevent corruption and protect ratepayers, advocates say.
This article is provided by Eye on Ohio, the nonprofit, nonpartisan Ohio Center for Journalism, in partnership with the nonprofit Energy News Network. Please join the free mailing lists for Eye on Ohio or the Energy News Network, as this helps provide more public service reporting.
Regulators taking proactive steps could reduce the risk of future utility corruption scandals like that which led to this winter’s guilty verdicts for former Ohio House speaker Larry Householder and lobbyist Matt Borges, say advocates.
Yet for now the Public Utilities Commission of Ohio is dealing only with specific cases linked to the current scandal surrounding Ohio’s coal and nuclear bailout law, House Bill 6. And the commission has halted action in those cases, after receiving requests from the U.S. Attorney’s office to have parties hold off on further pre-hearing fact-finding, called discovery.
The Office of the Ohio Consumers’ Counsel asked the commission to move ahead, now that the trial of Householder and Borges is over. FirstEnergy opposed further action in an April 17 filing.
Advocates worry about the message such inaction will send to other companies.
“The laws prevent corruption. The question is whether the penalties are severe enough that they serve as a deterrent. And so far, FirstEnergy hasn’t really been penalized at all,” said senior attorney Rob Kelter at the Environmental Law & Policy Center.
Because of the delay, “the commission in Ohio hasn’t done anything to make customers whole,” said Dave Pomerantz, executive director of the Energy and Policy Institute. “Certainly they shouldn’t allow FirstEnergy to start an ESP [Electric Security Plan] or rate case or anything until they complete those investigations.”
FirstEnergy filed its latest ESP case for rider charges on April 5, and the PUCO has already scheduled a technical conference for May 10.
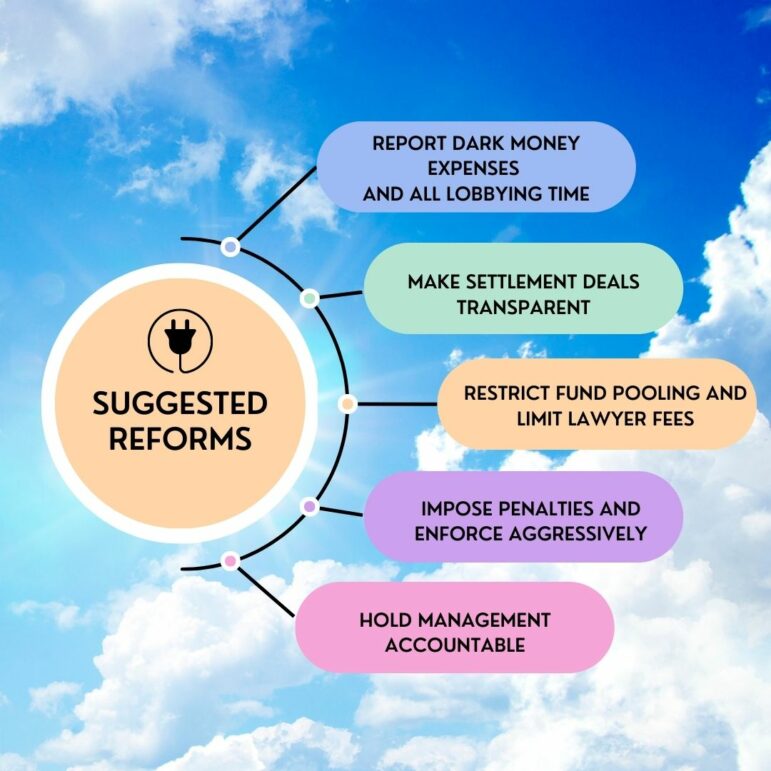
Aside from what happens in specific FirstEnergy cases, critics say the PUCO should take steps through rulemaking or otherwise to provide more transparency and accountability.
“The kindling that sets the fire is still sitting out there” with future opportunities for corruption, said Ned Hill, a professor of economic development at Ohio State University. In his view, common practices in Ohio utility regulation may not be illegal or corrupt per se, yet they are “corrupting.”
Shine a light on dark money
One step would be to require at least annual reporting of all political, charitable and advertising expenses by utilities, their parent corporations and affiliates. Critics say that reporting should include both reportable political contributions as well as dark money spending — money provided to organizations to influence political activity of any kind.
A 2010 Supreme Court case generally allowed unlimited corporate spending on political activities as long as it’s not directly coordinated with a candidate or campaign committee. And a 2021 ruling said states couldn’t require broad-based disclosures from all corporations.
However, regulated utilities are monopolies. And company operations are already supposed to be subject to a code of conduct, said Ashley Brown, a former PUCO commissioner who also headed the Harvard Electricity Policy Group. “So it’s just amending that code of conduct to say all political contributions of any kind, dark or otherwise, need to be disclosed.”
Additionally, Pomerantz would like regulators to require utilities, including parent corporations and affiliates, to report what percentage of time all staff and executives spend on rate and rider issues, lobbying, political activities, and other activities.
“The rules have to be really airtight. They have to define political influence activities pretty broadly,” or else companies will exploit any loopholes, Pomerantz said. Reporting requirements should be particularly strict for any “miscellaneous” spending categories, he added.
Regulators should also restrict any pooling of funds so that all ratepayer money is fully tracked, Pomerantz said. One pending FirstEnergy case involves the use of a joint money pool for roughly $450 million collected under a rider that was ultimately held unlawful.
The reports should be filed at least annually, so consumers’ advocates and other interested parties have ready access to information, Pomerantz said. Utilities frequently delay providing materials that consumer advocates and others seek in discovery, in apparent attempts to run the clock out and prevent follow-up investigations by those parties, he said.
FirstEnergy still has not provided the Office of the Ohio Consumers’ Counsel with some materials they initially requested more than two years ago.
Full disclosure on settlement deals
The PUCO’s practice generally has been to approve settlement deals in rate and rider cases. Critics say the commission should more closely scrutinize those deals and make sure all side agreements are fully disclosed.
“The commission rubber stamps every settlement,” Kelter said. “And the commission has shown no inclination to dig into the facts of how these settlements were reached.” Among other things, the PUCO is supposed to consider whether settlements were the result of serious bargaining. However, the commission is not admitting evidence related to that bargaining, so there’s no basis to make that conclusion.
“The PUCO has boiled this down to almost a Betty Crocker formula,” said Hill. A few interest groups or companies sign on in a “quid pro quo fest that says, ‘I’ll sign if you give me something in return.’” Those agreements, in turn, can trigger riders that the rest of the ratepayers wind up paying.
“I’m not saying it’s corrupt, because corrupt is illegal. But it’s corrupting,” Hill said. The bargains struck don’t benefit a large class, but just specific clients and specialized firms that represent them.
In 2015, for example, FirstEnergy utilities added new provisions to their proposal as several parties signed on to a partial settlement or dropped opposition to a plan to make ratepayers guarantee sales of electricity from the Davis-Besse nuclear plant, the Sammis coal plant and a share of two 1950s-era coal plants. The new additions would have given special rates or exemptions to a limited number of companies.
Ohio law also allows “reasonable arrangements to strike one-off rates for specific companies underneath the umbrella of economic development,” Hill continued. He would prefer for regulators to avoid those deals, but said at a minimum there should be full disclosure to the public.
“If you’re getting the public’s money, a business secret should not exist,” Hill said. “If you’re not willing to let daylight shine on the transaction, you shouldn’t get the money because you don’t need it.”
Other proposed reforms would whittle away some of the companies’ advantage in litigating rate and rider cases. A pending Connecticut bill would prohibit utilities from recovering attorney expenses, Pomerantz noted. As things stand, utilities often have whole cadres of lawyers ready to “litigate to oblivion,” while the Ohio Consumers’ Counsel is a state agency with a set budget, and advocates also have more limited budgets.
Hold management accountable
Regulators could call on companies to make changes in management, or to put in a receiver, Brown said. The PUCO did that in at least one Columbia Gas case back in 1985.
“Another thing [regulators] can do is ding the rate of return,” Brown said. Regulators let companies collect a percentage of their capital investments from ratepayers. But that rate can be adjusted if a company provides substandard service or has a history of poor management. And becoming embroiled in corruption charges would be a sign of poor management, he said.
The commission also could order funds for riders put into escrow and require utilities to seek reimbursement instead of getting all the money up front, Brown suggested. An audit in one of the FirstEnergy regulatory cases found that roughly one-fourth of nearly $25 million in rider charges reviewed in that case was improper.
In extreme cases, the state attorney general could take action to revoke a utility’s corporate charter, co-director Greg Coleridge of the Move to Amend coalition has argued.
The PUCO also retains authority over the monopoly granted to utilities. “The commission could easily do a show cause order” to require a utility to demonstrate why its license shouldn’t be revoked, Brown said.
Regulators could also impose penalties when utilities don’t strictly comply with the law. Ohio law already authorizes the commission to make companies pay triple the amount of damages, as well as penalties of $10,000 per day, challengers argued in one of the FirstEnergy cases in which rider money went into a money pool and was not properly tracked.
Indeed, if all utilities have to do is return or credit any unlawful charges, that’s akin to catching bank robbers inside a vault and telling them to just put back the money, Pomerantz and Kelter said. Otherwise, companies would have no incentive to avoid trying again.
“If the punishments aren’t severe enough, you’re sending utilities the wrong signals,” Kelter said.
‘In a deliberate manner’
The Energy News Network and Eye on Ohio asked the PUCO commissioners what steps, if any, they were taking to prevent future corruption cases, as well as whether they would oppose some of the steps described above. In response, spokesperson Matt Schilling referred to the four regulatory cases that have been stayed.
“The commission speaks through its written opinion and orders, and it would be inappropriate to speculate on the outcome of pending cases or address vague hypotheticals,” Schilling said. “In reaching its decisions, the Commission is bound by state law and the record of evidence in each case before it.”
Schilling also referred to prior entries by the commission, which said it would “act in a deliberate manner, based upon facts rather than speculation” and that it would “follow the facts wherever they lead.” He did not respond to a follow-up email.
“This is a dodge,” Pomerantz said after reading Schilling’s comment. “The idea that there isn’t enough out there to open a docket to prevent the next one [corruption scandal] is totally disingenuous.”

